What In The World Is HDR ?
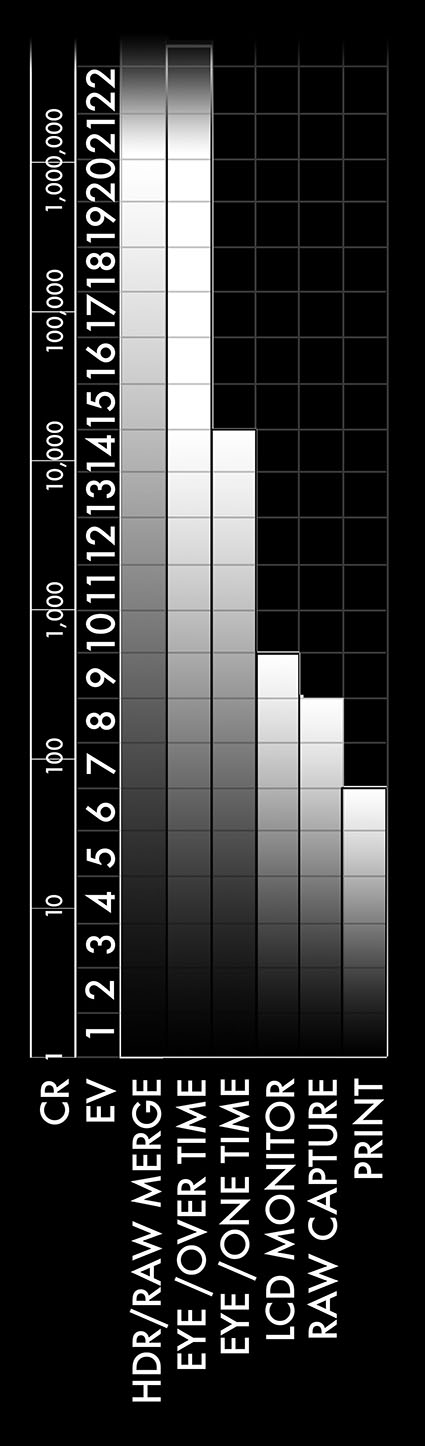
1 EV is equivalent to 1 F-Stop of brightness

These Contrast Ration (CR) figures are approximate
Dynamic Range
Today, many people think HDR refers to the practice of merging bracketed exposures with software, but HDR actually applies to everything in an imaging workflow - capture, processing, display, and printing.
What is HDR? HDR is an acronym that stands for High Dynamic Range. It’s the opposite of LDR or Low Dynamic Range Imaging.
What is dynamic range? In imaging, dynamic range (DR) is the highest overall level of contrast found in an image. In other fields, such as in the audio industry, dynamic range is used to describe similar phenomena. In audio, DR is defined as the logarithmic ratio between the largest readable signal and background noise. DR is akin to signal-to-noise ratio. In imaging, DR refers to the entire image. Consider an image a signal – and every signal has some noise.
The values used to specify dynamic range can be charted on multiple scales. Whatever language is used to describe this phenomenon, two critical factors must be addressed; the total range of brightness and the fineness of the steps used within the scale.
Two scales are most useful for images – exposure value and contrast ratio. Exposure value (EV) is easier to use while contrast ratios better display logarithmic increases in light intensities. Both refer to the same phenomenon – relative increase or decrease in brightness.
The EV scale makes it easy to compare the ratios rather than the big numbers of logarithmic progressions; each successive EV rating represents a doubling of values. The exposure value (EV) scale has been used by photographers for ages. The International Organization for Standards (ISO) defines EV 0 at an aperture size of 1 and a 1 second exposure time. The same EV can be achieved with any other combination of f-stop and shutter speed that produces the same amount of light.
‘The contrast ratio scale specifically delineates values; when you use this rating you instantly see how much greater each step in a progression is than the previous one because the numbers are so much bigger. You can convert EV to contrast ration or vice versa with the right formulas. 2 (power of EV) = contrast ratio (2*8=256 for a contrast ratio of 256:1) or EV=log10(contrast ratio)*3.32 (log10(4000)*3.32=12EV
Dynamic range, gamut, and bit-depth are often confused. Though related, they’re all different. Dynamic range refers to a total range of luminosity values. Gamut refers to a total color capacity, including saturation. Bit depth refers to the number of points of data between values or the fineness of the increments in the scale. Just because an image is wide gamut doesn’t mean it is HDR or has high bit depth, but it will contain more and potentially better data if it does. Just because an image is HDR doesn’t mean it is wide gamut and has high bit depth, but it will contain more and potentially better data if it does. You can’t convert low dynamic range, small gamut, low bit depth information to high bit depth, wide gamut, high dynamic range information. To get it and use it, you have to capture high-quality information upon exposure and preserve it throughout your workflow.



No Comments