Capture Sharpening
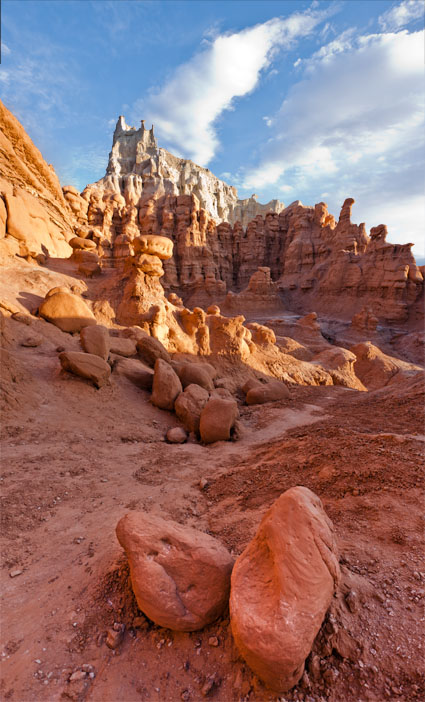

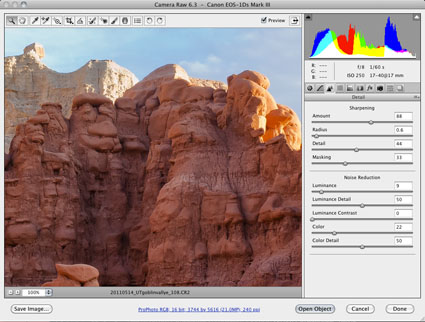
Optimal image sharpening is best done in three stages— capture (do it during RAW conversion), creative (do it in Photoshop) and output (automate it).
Capture sharpening benefits all images. It compensates for inherent deficiencies in optical and capture systems. All lenses and sensors have specific characteristics and deficiencies. They don't all have the same characteristics or deficiencies.
To speed your workflow, default settings for a best starting point for capture sharpening can be determined for all images created with the same lens/chip combination and saved for subsequent use. To optimally sharpen an image, you'll need to modify these settings to factor in additional considerations—variances in noise (ISO, exposure duration, temperature), noise-reduction settings and the frequencies of detail (low/smooth to high/fine texture) in an image.



