Photoshop’s New Filter Depth Blur Helps You Control Depth Of Field
Get My New eBook Global Warning Antarctica
47 pages – 36 images
A visualization of the invisible – greenhouse gases?
Or a visual metaphor for the negative emotions we are deluged with – solastalgia?
Global Warning Antarctica is a deep meditation on climate grief and eco-anxiety.
The environmental issues of our age are physical, social, ethical and also psychic issues.
12 Classic Mistakes We’ve All Made Trying To Make Better Prints

Plus 7 Extra Go To Printing Resources To Help You
Face it, we’ve all done it, that is overdone it, when we’re trying to make great prints. As important as it is to learn what you can do and how far you can go, it’s also important to learn how far not to go and why. You learn what to look for as well as what to look out for. These trials of error can be beneficial. You’re sure to learn a lot when you make mistakes. And we can learn from each other’s mistakes as well as our own. One of the many benefits of teaching printing for over twenty-five years is that I get to learn from my mistakes and from many other people’s too. There are some classic printing mistakes I see made time and time again because the approach is correct but the practice has just gone too far. If you’ve never made some of these mistakes, I recommend you make them – once.
Here are some classic mistakes I see so many people make when they’re printing – and the cures.

It’s Too Light
You want your print to be more luminous so brighter’s better right? But your image ends up looking washed out. The solution is to lighten the highlights more than the midtones and shadows. It’s a specific kind of contrast you won’t get with a Contrast slider but you will get with a Highlights slider or even better with Curves. You might also darkens shadows slightly. It’s the apparent contrast between highlights and shadows and in the midtones that will make your images glow. Most prints on average are weighted darker than middle gray so that their highlights will pop.
Whites Without Detail
So once again you’re chasing lightness and you push your highlights too far eliminating detail. There is a limit to how far you want to go and you just stepped over the line. Pull back. You can move in that general direction just don’t go so far. Don’t push the Whites slider so hard and pull your Highlights slider down a little, plus remember that you can get a second pass of Highlights and their neighbors Lights with Curves. You want highlights to have full detail and to be bright but not so bright you feel like you have to squint to see the picture better.


Whites Touch The Frame
Sometimes you have exposure that don’t have much (or any) detail in very bright areas. This is particularly problematic when they touch and break the rectangle of the frame. If you’re not going to clone detail into those areas, go old school and “fog” those areas, that is print them slightly gray. Using a brush lower the Whites slider (maybe the Highlights too) to build up some density without texture and restore the frame. You don’t need a lot, just enough to make the frame coherent, keeping the eye from wandering out of it and minimizing the distraction. Alternately, in Photoshop you can use a Curves adjustment layer and lower the white point slightly, then readjust the rest of the Curve to keep all the other tones glowing; paint on the mask to isolate this effect.
A Fast Way To Create Flares In Photoshop | Unmesh Dinda
4 Reasons Photographers Should Draw More Often

This drawing is beautifully rendered but drawing like this is an inefficient way to capture an idea.
Think of the difference between notes and finished pieces of writing. Both kinds of writing are useful. One kind of writing might even lead to the other. You don’t spend as much time choosing the words you put on a post-it note as you do the words in a job application. One kind of writing might even lead to the other. Because they take less time and skill, you make a lot more notes than you do finished pieces of writing.
Can you draw? Note that I didn’t ask you can you make drawings that look pretty. So if little kids can draw, then so can you! Think of these types of drawing (sketches, doodles, cartoons) as notes that require very little drawing skill. They’re most useful when you keep them simple. Their value is not as aesthetic objects but in the quality of thought they contain. But why would you want to? Let me count the ways.
1
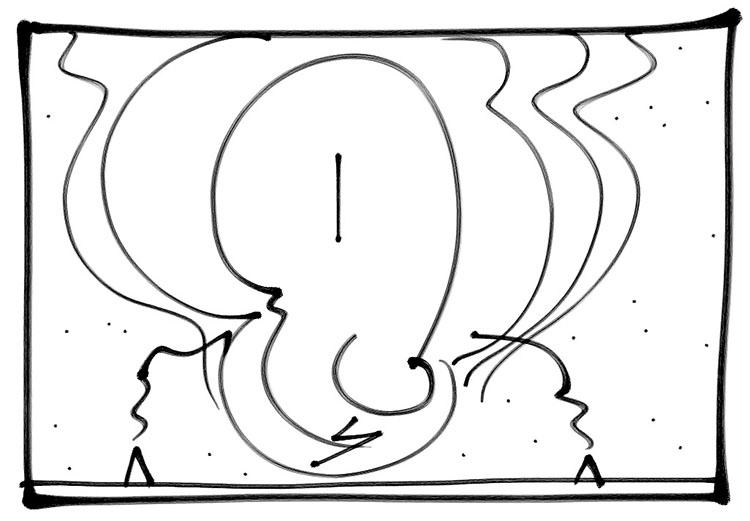
Imagine The Possibilities
Draw when you can’t get there from here or you can only imagine it.
(I could have recorded the idea with words but this simple image is much more specific.)
2
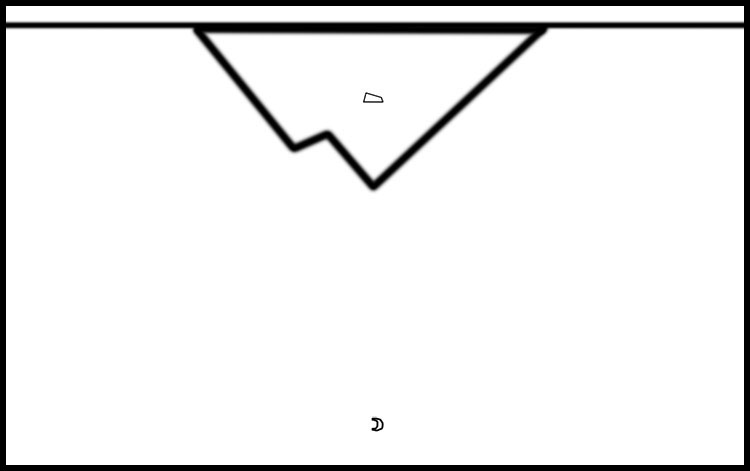
Capture The Idea In What’s Picture Imperfect
Draw when what you see isn’t picture perfect but you want to remember the idea.
(I saw this type of image many times before I encountered it with calm water and unbroken reflections.)
 3
3
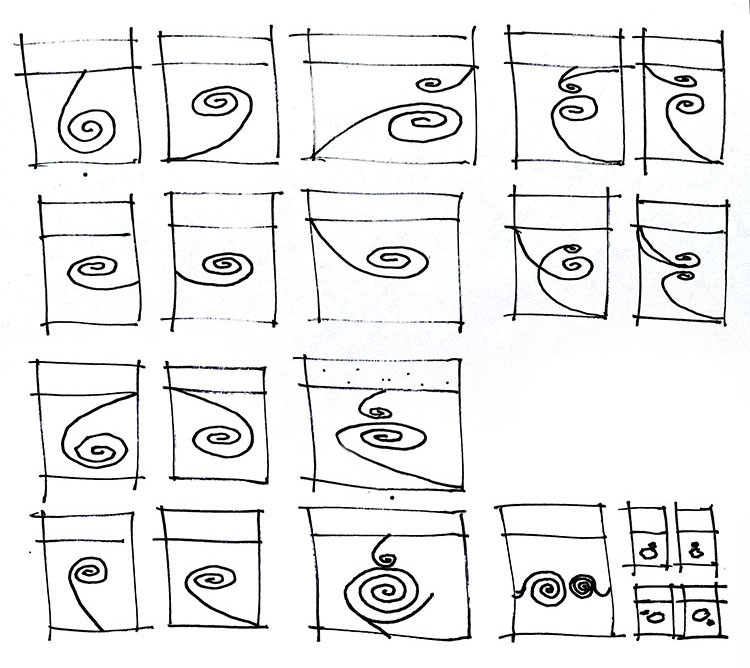
Identify Possible Variations
Draw when you want to figure out new variations of the same idea.
(Drawing helped me find the idea of not just one but two spirals.)


4
Structure Stories With Storyboards
Draw when you start a project and you want to figure out which shots you need to complete it.
(Storyboards are what great movie directors like Hitchcock and Spielberg use.)
Read more on Drawing here.
Let Why You Draw Determine How You Draw
If I’m trying to make a drawing that looks good or one that is good to look at then the hour I spent making this is well spent but if drawing requires that much time I won’t draw often.
If I’m drawing to record ideas, this is a much more efficient way to draw and so I’ll draw more.

“Make things as simple as possible – but not simpler.” – Albert Einstein
In their wonderful book Art & Fear Ted Orland and David Bayles share a story.
A daughter asks her father, “What did you do today?”
“I taught my students how to draw,’ he responded matter of factly.
She gasped in amazement, “When did they forget?”
I find that when I ask people if they can draw the number of affirmative responses is directly related to age. The younger you are the more you know you can draw. So what happens when we grow up? We are taught a terribly limiting understanding of the many things drawings can be and do.
With a unidimensional vision of what drawing is, we are trapped by someone else’s limited vision of perfection that is further complicated by comparison to others.
We can all draw. Note that I didn’t say we can or should all draw like Michaelangelo. It takes more time to develop the skills necessary to draw in some ways than others. And you probably draw a little differently than your friends who also think they can’t draw. But if you can read this (possibly even if you can’t), then chances are you already know more than one way to draw.
Drawing is many different things to many different people – and it can do many things for you. For Thomas Edison drawing was a way to visualize what didn’t exist – yet. He handed his team a very simple sketch to help them invent the phonograph. (As a draftsman he was no Leonardo but his limited drawing skills helped him be an even better inventor.) Words weren’t enough and he needed a way to visualize what they had never seen before but soon would in part because he helped his team visualize it with a drawing.
So once we understand that even doodles are just one of many kinds of drawings, we might start to reframe what makes a drawing good based on the purpose we intend it to serve. If all you’re looking for is a way to find and capture ideas, then the time it takes to render them realistically is wasted. (And who wants to waste time?) Moreover, for some purposes, the extra detail added may be distracting or, worse, confusing. (If I ask you where the bathroom is, and you start spouting extended passages of flowery verse, one or both of us might get wet.)
The kind of drawing I want to encourage you to practice as part of your creative toolkit is not about making good-looking drawings; it’s about making useful drawings. Drawing can be useful in many, many ways.
1. Imagine The Possibilities
2. Capture The Idea In What’s Picture Imperfect
3. Identify Possible Variations
4. Structure Stories With Storyboards
4 Good Books That Will Help You Make Faster Smarter Drawings

Want to up your drawing game? Want to just get some game – fast? Check out these books. These books are first and foremost about making drawings to find, refine, and record ideas; they’re about making useful drawings, not drawings that are meant to look good.
This book shows you how to draw quickly and effectively, as well as many different uses for drawing.
Drawing Ideas – Mark Baskinger + Willam Bardel
This book is much more than you need, but it’s still useful because it offers a number of reasons why to draw and how to draw based on those reasons.
Setting Up Your Shots – Jose Cruz
This isn’t officially a drawing book (and the drawings in them are … eh) but it offers a great clear survey of the different camera moves filmmakers use to tell stories. This knowledge will help you vary the way you compose your drawings for effect and with purpose. Think storyboards.
Visual Grammar – Christian Leborg
This composition book uses nothing more than simple shapes and lines to demonstrate the fundamentals of composition, which you can use to understand the dynamics of any image, generate new ideas, and make many variations on them.
Enjoy drawing!
Learn more in my photography and creativity workshops.
How Drawing Helps You Think | Ralph Ammer | TEDxTUM
“You don’t have to be an artist to draw! In this beautifully illustrated talk, Ralph Ammer shows how drawing your thoughts can be a powerful tool for improving your thinking, creativity, and communication. He wants you to believe in your drawing abilities and provides numerous exercises to help you get started.
Ralph Ammer is a professor at the Munich University of Applied Sciences and teaches biophilic design, which aims to create life-friendly objects, images, and services based on nature. Ralph believes in the diversity of 21st-century craftsmen, regardless of whether they produce well-written programming code, carefully crafted prints, or the occasional ceramic vessel.”
The One Simple Trick I Use To Improve All Of My Images With Photoshop

Before
After

Curves offers more precise tonal control than any other tool. So when I need precision dodging and burning (about 80% of the time) I use Curves, which means I use Photoshop (PS).
I look forward to the day we can make local adjustments with Curves in Lightroom and Camera Raw. But currently, Lightroom (LR) and Camera Raw (ACR) don’t have this feature, yet. But can’t you do something similar in Lightroom (LR) or Adobe Camera Raw’s (ACR) using the six Basics sliders (Exposure, Contrast, Highlights, Shadows, Whites, Blacks), in combination with the Adjustment Brush, Graduated Filter, or Radial Filter, even in combination with Color, Luminance, or Depth Range Masks? If close is good enough, yes. If you want to make your images really shine, no.
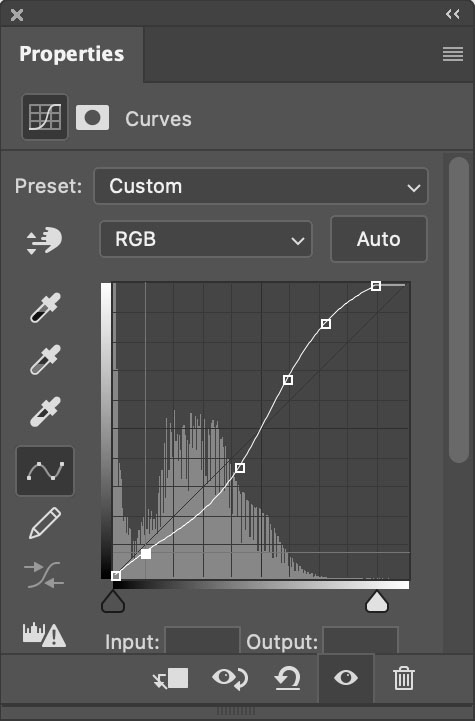
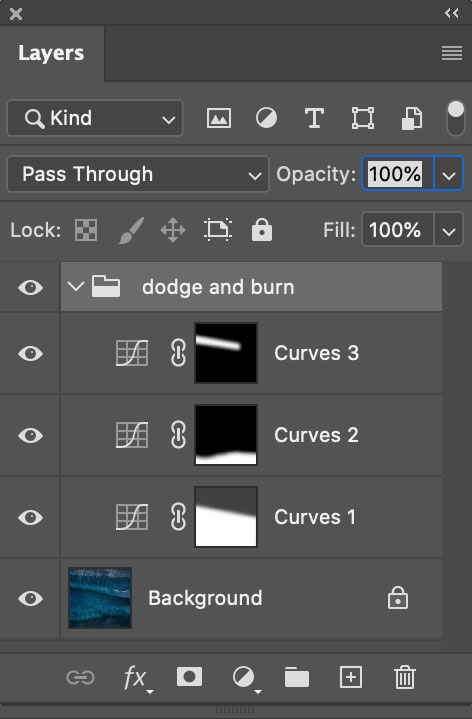
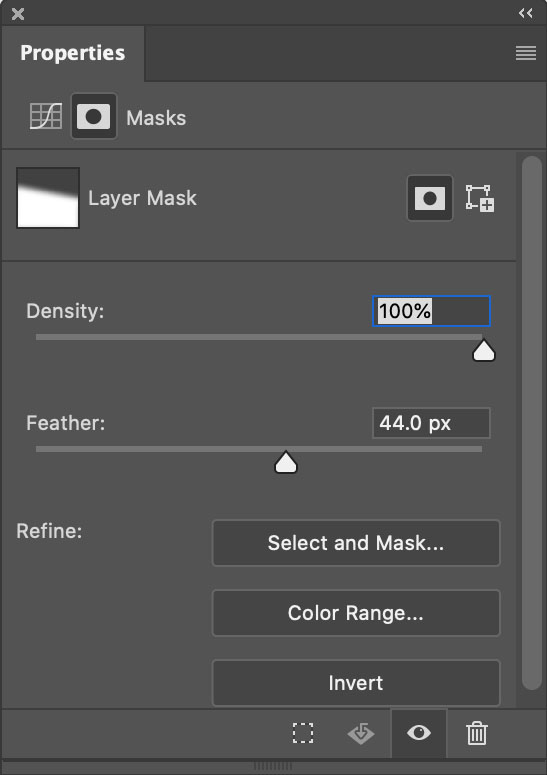
Is it hard to dodge and burn with Curves in Photoshop? No. It’s easy.











