Reduce Noise With Multiple Shots

Got noise in one exposure? Make a bunch of exposures and watch the noise disappear.
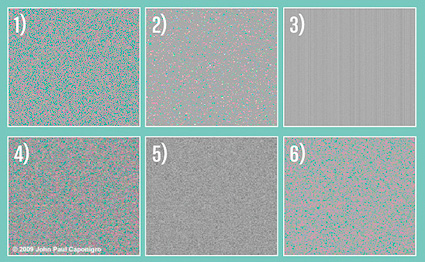
You can reduce noise in an image by combining multiple exposures of the same composition in Photoshop. Photoshop can search for the differences between the separate exposures and then blend them, keeping what stays the same and eliminating what changes. Random noise between separate exposures of the same composition will be substantially, even dramatically, reduced or disappear altogether. (This technique won’t eliminate fixed noise, hot pixels, or column and row noise. There are other techniques for that, like using dark slides.)
You’ll find having this option will greatly reduce any reluctance you have toward using high ISOs. This means two things. You’ll be able to make images in lighting situations you thought you couldn’t, and you’ll be able to make handheld exposures in conditions you ordinarily wouldn’t be able to without severely compromising quality.
So how do you do this? Use the following steps.
1. Shoot multiple exposures.
Try to minimize camera motion as much as possible. It’s not necessary to use a tripod, but it’s helpful2
2. In Photoshop, go to File > Scripts > Load Files into Stack.
3. Click Browse and select the exposures to be used in the Stack and check Attempt to Automatically Align Source Images and Create Smart Object after Loading Layers.
This will create a single Smart Object from the multiple exposures. Double-clicking on this Smart Object will allow you to see the layers separately.
4. Go to Layer > Smart Objects > Image Stack Mode > Median to blend the separate exposures.
You’ll see that the noise is re-duced substantially.
5. Optionally, compare Image Stack Mode > Mean.
This works best for exposures containing no movement.
Read more about this technique at Digital Photo Pro.
Learn more about noise here.
Learn more in my digital printing workshops.